(1471 products available)

























































 Ready to Ship
Ready to Ship




































































































 Ready to Ship
Ready to Ship





An electronic TR igniter is a device used to ignite fuel in gas appliances, typically utilizing a high-voltage electrical spark. The main types of TR igniters include:
Ceramic Igniters
Ceramic TR igniters, also known as ''spark plugs,'' have a durable, heat-resistant ceramic body. They generate a high-voltage spark when triggered by a continuous electrical supply, making them suitable for industrial furnaces and other applications where reliable ignition is needed.
Metallic Igniter
Metallic TR igniters are made from metal components such as stainless steel or nickel alloys. They are designed to withstand harsh environments and corrosive flue gases, making them suitable for applications where durability and reliability in challenging conditions are required.
Coil Igniter
Coil TR Igniters utilize an electrical coil to generate a high-voltage spark when energized. They are compact and lightweight, making them suitable for applications where space constraints are critical.
Electrode Igniter
Electrode TR Igniters utilize one or more electrodes to generate a spark when subjected to a high-voltage electrical pulse. The arrangement and spacing of the electrodes are designed to optimize spark generation and fuel ignition efficiency.
Hot Surface Igniter
Hot surface TR igniters use resistive heating elements (often made of silicon carbide) to reach high temperatures. They rely on direct electrical current heating the elements to glow and ignite fuel upon contact. These igniters are known for their low emissions and quiet operation, making them suitable for applications with environmental noise concerns.
Silicon Carbide Igniter
Silicon carbide TR igniters utilize silicon carbide (SiC) as the primary material for the ignition element. SiC has excellent thermal stability and can withstand high temperatures and harsh operating environments. These igniters are particularly suitable for applications with stringent reliability and durability requirements.
Capacitive Igniter
Capacitive TR igniters incorporate capacitive components to store electrical energy and discharge it as a pulse during ignition attempts. This stored energy enhances spark intensity, increasing the likelihood of fuel ignition, especially in challenging conditions or with difficult-to-ignite fuel types.
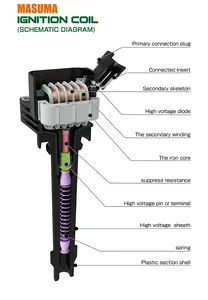
Specifications of TR ignition coils:
Voltage output:
TR ignition coils have high and low voltage outputs. The high voltage is about 20,000 to 45,000 volts. This voltage can cause a spark that ignites the fuel and air mixture in the engine. The low voltage output is around 10,000 to 25,000 volts. This lower voltage is used for smaller engines or when the engine is idling.
Coil resistance:
The coil resistance of TR ignition coils is between 0.5 and 2 ohms. This low resistance allows a large current to flow through the coil. The current builds up a strong magnetic field, which produces a more powerful spark. The low resistance also means the coil heats up less.
Turn ratio:
The turns ratio is how many times the primary winding wraps around the secondary winding in the coil. For TR ignition coils, the turns ratio is typically 100:1 to 250:1. This means the secondary winding has 100 to 250 times more loops than the primary. The turns ratio increases the voltage from the battery before sending it out as a spark.
Coil size:
The size of a TR ignition coil can vary depending on the engine it is used for. Generally, they are 4 to 6 inches long and 2 to 4 inches wide. The coils are also encased in a plastic or metal housing that protects the windings and electrical connections.
TR ignition coil maintenance
1. Regular inspection:
It is essential to check the ignition coils regularly. Look for signs like cracks, oil leaks, or damage. The spark plugs and wires should also be examined to ensure they are in good condition. Worn spark plugs can cause misfires, while damaged wires may result in weak or no sparks.
2. Proper gap adjustment:
Check that the gap between the spark plug electrodes is set correctly. An incorrect gap can lead to inefficient combustion or engine performance. Refer to the vehicle's manual for the correct specifications.
3. Cleanliness:
Keep the ignition system clean. Dirt and grime can cause problems over time. Use a dry cloth or a little rubbing alcohol to clean. Avoid using moisture or liquids that can damage the coils or other components.
4. Proper torque:
Ensure that the bolts or screws holding the ignition coils in place are tightened to the right force. Loose fasteners can lead to coil movement and intermittent spark issues.
5. Prevent oil and moisture exposure:
Keep the ignition coils away from oil leaks and excess moisture. Oil can break down the insulating material over time, while moisture can cause electrical problems. If there are any oil leaks in the ignition coil area, have them fixed promptly.
6. Follow the manufacturer's maintenance schedule:
Adhere to the recommended maintenance schedule provided by the coil's manufacturer. This may include periodic inspections, cleaning, and, if necessary, replacement of specific components to ensure optimal ignition system performance.
7. Use quality replacement parts:
If a replacement ignition coil or other components are needed, select high-quality components that meet or exceed the original equipment specifications. This ensures reliability and durability in the ignition system.
Fuel Type
Consider the vehicle's fuel type when selecting a TRD ignition coil. Gasoline engines generally require a standard coil, while turbocharged or premium fuel-burning engines may benefit from a high-performance coil for better spark delivery.
Engine Modifications
For vehicles with significant modifications (e.g., aftermarket intakes, exhausts, or engine tuning), upgrading to a TRD ignition coil may be advantageous. The coil can provide a more robust spark to support increased power from modified components.
Driving Conditions
Consider typical driving conditions and habits as well. Those who drive short distances in stop-and-go traffic may need a coil that provides easy, low-speed spark. Off-road, towing, or track enthusiasts may require a coil that can deliver consistent spark under high loads or extreme conditions.
Coil Specifications
When selecting a coil, review specifications such as voltage output (should match or exceed factory levels), resistance values, and any performance claims from the manufacturer. Choose a coil with ratings appropriate for the vehicle's engine requirements.
Compatibility
Ensure that the TRD ignition coil is compatible with the vehicle's make, model, and engine type. Check the specifications and fitment options to avoid any issues during installation.
Quality and Reliability
Choose a TRD ignition coil from a reputable brand known for its quality and reliability. This ensures that the coil will perform consistently and withstand the demands of high-performance applications.
Warranties and Guarantees
Check if the TRD ignition coil comes with a warranty or guarantee. This provides an added layer of assurance regarding the quality and performance of the product.
Turn Off Gas Supply
Before any work is done on a gas stove, safety must come first. To avoid any gas leaks or accidents, make sure to turn off the gas supply to the stove.
Unplug the Stove
It is important to disconnect the stove from the electrical supply. This will prevent any electrical accidents from happening while working on the stove.
Remove Burner Grates and Caps
The next step is to take off the burner grates and caps. This will allow access to the igniter components that need to be replaced or repaired.
Access the Igniter
Depending on the stove model, the igniter might be located underneath the burner head or attached to its side. Use a screwdriver to remove any covers or screws holding the igniter in place to access it.
Inspect the Igniter
Once the igniter is exposed, inspect it for any visible signs of damage, such as cracks or corrosion. If the igniter is worn out, it should be replaced with a new one. Before installing a new igniter, ensure the area is clean and free of debris.
Reconnect Wires
If the wires leading to the igniter are loose or disconnected, carefully reconnect them. Ensure they are securely attached to prevent any ignition issues.
Test the Igniter
Before reassembling the stove, plug it back into the electrical supply and turn on the gas to ensure the igniter functions correctly. Exercise caution during this step and follow all safety guidelines related to gas appliances.
Reassemble the Stove
Once it has been confirmed that the igniter is working properly, reassemble the stove by putting back any covers or screws that were removed. Replace the burner caps and grates.
Restore Gas and Electrical Supply
Finally, turn the gas supply back on and reconnect the stove to the electrical supply. The stove should now be ready for use.
Q1: How can one know a proper TRQ igniter coil has been fitted in an engine?
A1: When a proper TRQ igniter coil has been fitted in an engine, users will notice proper engine performance. Signs of engine failure or disturbances will be absent. The engine may also sound different as a sign of smooth operation.
Q2: How long does a proper TRQ igniter coil last?
A2: Proper TRQ igniter coils are designed to last between 100,000 to 200,000 miles. Their longevity depends on factors such as driving conditions and engine maintenance.
Q3: What should be done when a TRQ igniter coil gets faulty?
A3: When a TRQ igniter coil gets faulty, users should rush to have it replaced. Ignoring a faulty coil can cause damage to other engine parts such as the spark plugs and can also affect engine performance.
Q4: Can all types of igniters work on every engine?
A4: No. Not all igniters can work on every engine. Coils are designed to be compatible with specific engine models. It is important to choose an igniter coil that matches the coil's make, model, and year.
Q5: Can a faulty TRQ igniter coil be repaired?
A5: No. TRQ igniter coils are not recommended to be repaired. Once they lose functionality, users should go for replacement as the best solution.