(911 products available)









































































































































































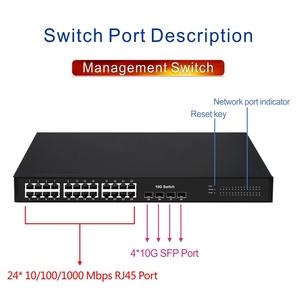



















































A 24 port L2 switch comes in different models that operate at layer 2 of the OSI model. These models provide businesses with options that can meet their needs and budgets. The L2 switch with 24 ports is available in the managed, unmanaged, and stacking models.
Managed Layer 2 Switch
A managed layer 2 switch provides businesses with a secure and efficient network. The switches regulate network traffic and enhance its performance. Administrators can control and configure the switch using an encrypted management protocol. The protocol offers tight control over the switch's operation. Layer 2 switches allow the implementation of VLANs for network segmentation. Virtual networks are created on a physical network to improve performance and enhance security. A managed switch offers administrators good insight into network operation.
They have excellent monitoring and troubleshooting tools. Managed layer 2 switches allow the implementation of security measures that prevent unauthorized access. Administrators can set up different access levels.
Unmanaged Layer 2 Switch
An unmanaged switch operates at layer 2 of the OSI model without any control. It is ideal for small businesses and simple networks. The switches provide plug-and-play connectivity between networked devices. Unmanaged switches facilitate encrypted data transfer between devices. They have no management interface for monitoring data transfer. However, these switches route data packets between devices for fast data transfer. Unmanaged layer 2 switches provide basic data transfer essential for all networked computers, printers, and servers to operate.
Stacking Layer 2 Switch
A stacking switch consists of multiple identical switches that can be combined into a single unit. Each switch in the stack functions independently and can be managed from one IP address. Stacking switches provide flexibility and scalability for business networks. They enhance network performance by providing additional processing capacity. Layer 2 stacking switches integrate different networks to promote resource sharing. The switches offer reliable data transfer and reduce network latency. Traffic between users, applications, and devices run over a single network. Stacking layer 2 switches improve data throughput and reduce costs by consolidating infrastructure.
Layer 2 switches with 24 ports harness the power of switching technology to connect multiple devices within the same network, or segment a network, thereby improving network performance and capacity. A 24-port L2 switch operates at the data link layer of the OSI model to create a separate collision domain for each port. Here are some of the common functions and features.
VLAN Support
Virtual local area networks (VLANs) segment large networks to increase efficiency and security. VLANs group multiple users by function, project team, or department, regardless of their physical location. They also prevent sensitive data from being accessed by unauthorized users, thereby improving network performance.
Link Aggregation
Link aggregation or trunking combines several physical links into a single logical link to increase bandwidth and provide redundancy. Administrators can increase bandwidth between switches, servers, or storage systems without adding more cables or network interfaces.
Quality of Service
Layer 2 switches prioritize and control bandwidth for sensitive applications that run in real time, such as Voice over IP (VoIP) or video conferencing. They can classify and mark traffic to ensure that time-sensitive data is transmitted over the network quickly and with minimal latency.
Port Mirroring
Port mirroring is an essential feature for monitoring and troubleshooting networks. It copies the traffic on one port to another for analysis or troubleshooting. Network administrators can use it to monitor network performance, detect or analyze malicious activity, and troubleshoot network issues.
STP
Spanning Tree Protocol detects and eliminates loops in a switched or bridged network with redundant links. STP puts some ports in a standby state to ensure there is a loop-free logical topology and retains a backup link to maintain network availability if the active link fails.
Flood Control
Flood control limits the amount of broadcast or multicast traffic a switch can forward to prevent network disruption. A lot of broadcast or multicast traffic can reduce network performance and cause service degradation; flood control ensures that the network remains stable and responsive.
Network Access Control
Network access control authenticates, authorizes, and enforces security policies for devices and users trying to access the network. It ensures only authorized users and devices access the network, preventing data breaches, protecting sensitive data, and ensuring compliance with industry regulations.
PoE
Power over Ethernet (PoE) delivers power and data over the same Ethernet cable to devices like IP cameras and wireless access points. It simplifies the deployment of networked devices in locations where power outlets are not easily accessible. PoE eliminates the need for electrical contractors or additional power wiring.
Layer 2 switches with 24 ports can be used in industries like:
Office Networks
Layer 2 switches make it easier for workers to connect their computers, printers, and phones around the office.
Schools
In schools, Layer 2 switches connect different computer labs, libraries, and classrooms so students can use the internet and educational programs.
Shops and Businesses
Businesses use these switches to connect security cameras, point-of-sale systems, and inventory scanners to keep an eye on customers and track supplies.
Hospitals
Layer 2 switches connect important tools and machines so doctors can check patients and share medical records wherever needed.
Manufacturing
Factories use Layer 2 switches to connect machines, computers, and hand-held scanners to keep operations running smoothly and track parts and equipment.
Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP)
Switches can establish a tunneling protocol to create virtual private networks and connect remote offices securely over the internet.
ISP Networks
Internet service providers utilize VLANs on Layer 2 switches to efficiently manage and segment network resources for different customers.
Gaming Centers
Layer 2 switches can be installed in video gaming centers to assist in connecting multiple game consoles, PCs, and gaming peripherals for smooth multiplayer gaming and competitions.
Cybersecurity Training Facilities
Cybersecurity training centers use Layer 2 switches to create isolated virtual networks for hands-on training in network security and attack-defense scenarios.
Any place that requires a wired network can use 24-port Layer 2 switches. They provide a reliable way for multiple devices to communicate with each other.
Purpose:
Think about the jobs that need to be done before picking the switch. Layer 2 switches are basic for interfacing a lot of clients or gadgets inside a similar organization. Layer 2 works at the Ethernet level and is utilized for nearby organizations. Nonetheless, in the event that the organization needs web access or to move information between different areas, a Layer 3 switch is required in light of the fact that it can course traffic between different organizations. Layer 3 works at both the Ethernet and the Internet Protocol level, giving more highlights. Layer 3 switches are significantly more costly, so Layer 2 is the correct decision on the off chance that just nearby movement will be moved.
The two switches need to be evaluated on their details, which significantly affect execution, like the information exchange rate and throughput. The information exchange rate tells how quick data is sent over the organization, and the throughput tells how much information is prepared. These two numbers ought to be high to keep the organization running easily without delays when a ton of clients are utilizing it simultaneously. It is likewise critical to check what number of edges each switch can handle, called edge for every second. This shows how well it can move information without halting.
Sizes of 24 refer to the amount of ports on a switch. It is explained in the number model, where L2 is a limitation of two fluids, and these have been recognized through the determination of Standard Ethernet or Criteria of Gigabit Ethernet.
Management:
Managed switches are useful for having more control over the organization. Overseen ones let clients see what's going on, change settings, and safeguard the organization with private passwords, while uncontrolled ones just let data out. Unmanaged switches are acceptable for straightforward organizations that need to deal with expenses and intricacies, while managed networks require innovation and make work the executives more straightforward. Layer 2 and Layer 3 use the two, but only Managed can be configured.
Benefits of Layer 2:
Layer 2 switch benefits include improved network efficiency, enhanced data transfer, and reduced costs throughcale clustering. In the past, many local area networks used Layer 2 Ethernet switches. A Layer 2 switch Ethernet can act as a multiport bridge, transferring frames from one port to another based on MAC addresses. Layer 2 works at the data link layer of the OSI model, where Ethernet and switches reside. Layer 2 switches use MAC addresses to forward frames, filtering and forwarding based on the addresses learned from incoming frames. They provide a way to segment collision domains, reducing traffic and improving performance. Layer 2 switching is faster than traditional bridging, making it more efficient.
Q1: What security challenges do L2 switches face, and how can they be mitigated?
A1: Unauthorized access and data breaches are among the security challenges faced by the switches. These poses significant risks to network integrity and data confidentiality. To mitigate such challenges, implementing robust security measures like regularly updating firmware and software to strengthen system vulnerabilities is critical. Moreover, integrating access control measures, such as incorporating switch port security, ensures only authorized devices and users can access the network. In addition, encrypted protocols, including SSH and SNMP version , safeguard sensitive data by preventing unauthorized entities from accessing credentials and system information.
Q2: What factors should be considered when selecting an L2 Ethernet switch?
A2: When picking an L2 Ethernet switch, a few factors need to be considered to ensure it meets network requirements and provides optimal performance. They include: Number of ports needed to connect devices in the network. Port speed to provide sufficient bandwidth for network traffic. Power over Ethernet capability to deliver power to VoIP phones, wireless access points, and IP cameras. Uplink ports for connecting to higher-speed networks. Managed or unmanaged switch based on the level of control and configuration options required. Budget ensuring the switch provides good value for money while staying within the budget.
Q3: Can Layer 2 switches be used to segment a network for improved security?
A3: Yes, Layer 2 switches can be used to segment a network for improved security. Network segmentation helps enhance security by controlling traffic flow between different segments and reducing the attack surface. VLAN configuration allows the creation of virtual networks within a switch, providing the ability to segment critical systems and departmental resources. Policies and controls are implemented to ensure each segment's security posture is maintained. For example, access control lists (ACLs) can be utilized to enforce security policies that govern traffic between VLANs or segments, ensuring only authorized entities can communicate.